Chicken Pox
After the first infection, the virus doesn't leave the body but instead goes into hiding in the nerve tissues. It can reappear later in life as shingles, a condition marked by painful skin rashes and blisters, particularly affecting older adults.
If you think you or your child might have chickenpox, it's important to consult a healthcare professional such as a general practitioner, pediatrician, or infectious disease specialist. They can provide guidance on managing the illness and easing symptoms.
For those concerned about skin issues during recovery, Pinnacle Dermatology offers specialized care. Our team of dermatology experts can create a customized treatment plan to address scarring and other skin-related problems, helping ensure a smoother recovery. With our advanced treatments and dedicated care, we aim to support you through every step of the healing process.
Examples of Chicken Pox
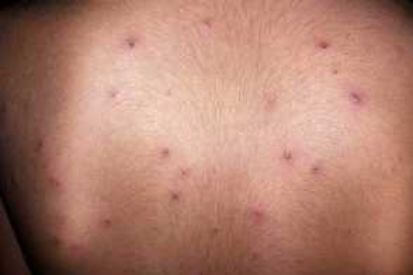
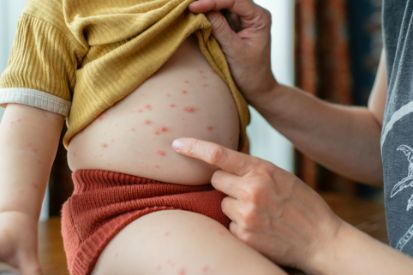
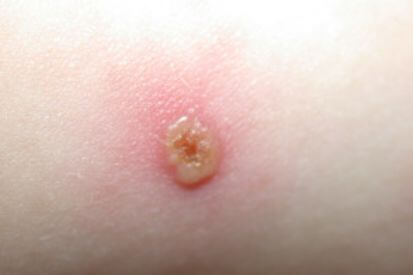
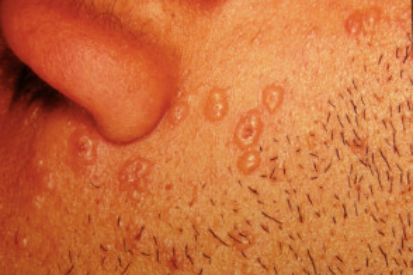
What are the Symptoms of Chickenpox?
- Rash: Itchy rash or red spots on the face, chest, and back before spreading to other parts of the body.
- Fever: Many individuals with chickenpox develop a moderate to high fever.
- Fatigue.
- Headache: Headaches may occur.
- Loss of Appetite: People with chickenpox may have a reduced desire to eat.
- Sore Throat: A mild sore throat can occur.
Causes of Chickenpox
- Chickenpox is caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV).
- It is highly contagious and spreads through respiratory droplets from infected individuals.
- Direct contact with the fluid from chickenpox blisters can also transmit the virus.
- The virus can be airborne, making it easily transmissible in crowded environments.
How to Prevent Chickenpox
Chicken Pox FAQs
Yes, chickenpox can cause scarring, particularly if the blisters are scratched or become infected. The characteristic itchy red spots and fluid-filled blisters can be quite uncomfortable, leading many individuals, especially children, to scratch them. This scratching can break the blisters open, introducing bacteria and causing secondary infections that increase the risk of scarring. Even without infection, scratching can disrupt the natural healing process of the skin, leading to pockmarks or indented scars.
In addition to mechanical damage from scratching, the severity and extent of the chickenpox rash can also influence the likelihood of scarring. More severe cases, where the rash is extensive and includes numerous large blisters, are more likely to result in permanent skin changes. To minimize the risk of scarring, it's essential to keep the skin clean, avoid scratching, and use soothing lotions or antihistamines to control itching. In cases where scarring does occur, dermatological treatments such as topical creams, laser therapy, or other procedures can help improve the skin's appearance.
In most cases, individuals with chickenpox can effectively manage their symptoms and recovery with the help of general healthcare providers, such as pediatricians or family medicine physicians. These professionals are well-equipped to handle the typical presentation of chickenpox and can provide guidance on symptom relief and prevention of complications.
However, there are certain situations where consulting a dermatologist may be beneficial. If you experience severe itching that does not respond to standard treatments, a dermatologist can offer specialized care to alleviate discomfort and prevent scratching that could lead to scarring. Additionally, individuals in specific populations, such as pregnant women, adults, or those with weakened immune systems, may require more specialized attention to manage their condition safely and effectively.
If you have concerns about the progression of chickenpox or complications arising from the illness, it is important to contact your primary healthcare provider first. They can assess your situation and determine if involving a dermatologist or other specialists is necessary. By working closely with your primary healthcare provider, you can ensure a comprehensive approach to managing chickenpox and minimizing any potential long-term effects on your skin.
Relieving the itching caused by chickenpox can significantly improve comfort and prevent complications like scarring from excessive scratching. One of the most effective methods is the use of topical treatments such as calamine lotion, which can soothe irritated skin and reduce itching. Over-the-counter antihistamines like diphenhydramine (Benadryl) can also help alleviate itching by blocking the histamines that cause the sensation. Additionally, keeping the skin clean and dry is important; regular, gentle bathing with lukewarm water and adding baking soda or colloidal oatmeal to the bath can provide further relief.
Applying cool compresses to the affected areas can help reduce inflammation and provide a soothing effect. It’s also advisable to keep fingernails trimmed short to minimize damage if scratching occurs. Wearing loose, comfortable clothing made of natural fibers like cotton can prevent further irritation of the skin. In severe cases, a healthcare provider may prescribe stronger antihistamines or topical steroids to manage the itching more effectively. Combining these approaches can help manage chickenpox itching and promote a more comfortable recovery.
How do you Treat Chickenpox?
While dermatologists primarily specialize in skin conditions, they may not be the first line of care for chickenpox. General practitioners, pediatricians, or infectious disease specialists often manage chickenpox cases. However, if complications arise, or if there are concerns about scarring or skin-related issues during the recovery phase, one of our dermatologists may become involved in the treatment plan.
Related Blog Posts

- Skin Cancer
- Sun Safety
Summer safety is more than just putting on sunscreen; many other factors to consider when keeping yourself and your children safe from damage and potential skin cancer.
- General Dermatology
- Skin Exams
Preparing for your first dermatology appointment is important because it ensures everything goes as smoothly as possible and that your doctor is up-to-date on the status of your overall health and wellbeing. Here are our expert tips.
Read More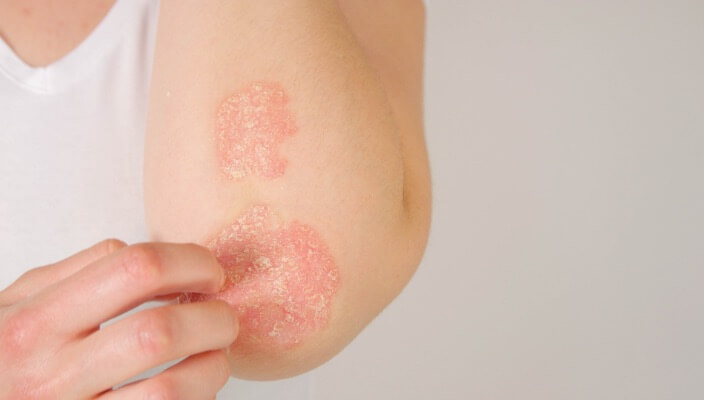
- General Dermatology
- Chronic Skin Conditions
Learn the differences between dry skin, eczema, and psoriasis, their distinct characteristics, and potential triggers. Gain valuable insights into identifying symptoms and seeking appropriate treatment to effectively managing these common skin conditions.
Read MoreFeatured Products
Check your local office for current stock!
Check your local office for current stock!
